iOS 개발자가 되기위한 Swift 톺아보기, Swift란 어떤 언어인지 가볍게 알아보며 핵심 중 하나인 Optional을 공부해보자.
- Swift
- iOS 개발자 로드맵
- 복합 데이터 구조
- 연산자
- 흐름 제어
1. Swift
Apple은 기존에 objective-c를 사용해왔고 호환성에 의하여 Swift는 objective-c 의 영향을 가장 많이 받았다.
Static Typing + Duck-type System
강타입이지만, duck-type system을 사용해 프로토콜을 채용해서 원하는 타입으로 변경이 가능하다.
타입추론
양방향 - 함수를 호출할 때, 안으로 들어가는 타입들을 바깥에 있는 타입으로 안의 타입을 유추할 수 있다? 안에 있는 타입을 리턴할 때, 리턴 타입을 가지고 바깥 타입을 추론할 수 있다.
타입추론은 컴파일러가 타입추론한다고 생각하자.
안전성
타입 안정성, 포인터도 타입으로 쓴다, Optionals
Functional Programming
Closures, Currying …
2. iOS 개발자 로드맵
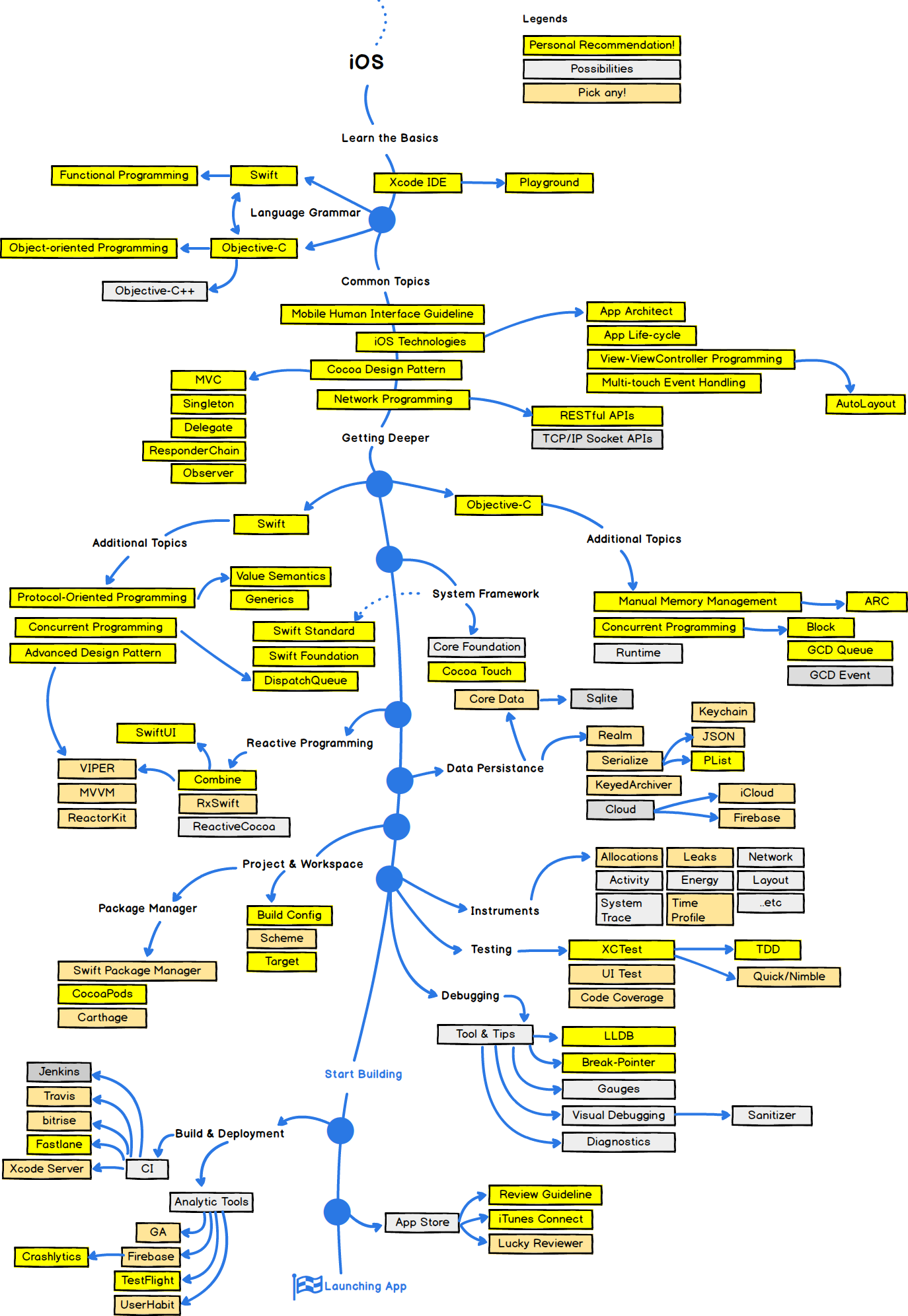
3. 복합 데이터 구조
tuples
여러 값을 한꺼번에 묶어서 사용하는 타입
let myPoint = (3, 3)
let myInfo = ("Cory", 99)
typealias PersonInfoTuple = (name: String, age: Int)
let cory: PersonInfoTuple = ("Cory", 99)
print("\(cory.0) is \(cory.1) years old")
enum
정의한 항목 값 중에 선택하는 타입
- 제한된 선택지 주고 싶을 때
- 정해진 값 외에는 받고 싶지 않을 때
- 예상된 입력 값이 한정되어 있을 때
기본 방식
enum Classes {
case algebra
case algorithm
case physics
}
원시값 raw-value
enum ASCIIControlCharacter: Character {
case newLine = "\n"
case tab = "\t"
}
array, dictionary, set
array
동일한 데이터 타입을 연속으로 담아 순서대로 접근하는 콜렉션
var grades = [90, 50, 70, 80]
dictionary
동일한 데이터 타입을 키값과 함께 담아놓고 키값으로 접근
var gradeDictionary = ["physics": 100, "algorithm": 97, "algebra": 88]
print(gradeDictionary["algorithm"] ?? 0)
set
동일한 데이터 타입을 순서없이 set에 넣고 중복여부를 파악
var classes = ["physics", "algorithm", "algebra"]
classes.contains("physics")
set은 array와 비슷한데, 배열과 비교해 중복을 확인하는 것에 대해 빠르다.
4. 연산자
삼항 연산자
Nil-coalescing operator (kow ・ uh ・ leh ・ suhng) coalesce : 합동하다. 연합하다
z = a ?? b
z = (a != nil) ? a! : b
고급 연산자
오버 플로우 연산
&+ , &- , &*
오버 플로우 되지 않는다.
5. 흐름 제어
if, switch-case
if 한줄이여도 중괄호 생략 못한다.
switch-case가 다른 언어에 비해 조금 확장되어있다.
switch-case에 쓰일 변수의 타입이 거의 어떤 것이든 상관 없고, case에서 범위도 가능하다.
for문
역방향은 stride를 사용한다
print() new line 없이 출력하는 법은 terminator를 활용하면 된다.
6. Optional
let possibleNumber = "123"
let convertedNumber = Int(possibleNumber)
convertedNumber는 optional Int이다. String안에 숫자 외에 다른 값이 있다면 nil이 될 수 있기 때문이다.
Optional이란 Boxing 개념이 있는데, binding은 이 box를 없애는 것
IUO : Implicitly Unwrapped Optionals
let assumedString: String! = "An implicitly unwrapped optional string."
let implicitString: String = assumedString // no need for an exclamation mark
Error Handling
함수 선언할 때 throws 있으면 do try
func makeASandwich() throws {
// ...
}
do {
try makeASandwich()
eatASandwich()
} catch SandwichError.outOfCleanDishes {
washDishes()
} catch SandwichError.missingIngredients(let ingredients) {
buyGroceries(ingredients)
}
func buyASandwich() -> Sandwich? throws {
var mySandwich : Sandwich? = nil
if (...) throw SandwichError.outOfCleanDishes
return mySandwich
}
let resultOptional = try? buyASandwich()
let resultValue = try! buyASandwich()
리턴값이 있으면 catch를 생략 가능
!치면 !를 작성한 사람이 책임진다 라고 느낌이 있다.



댓글남기기